Sigradur G Glassy Carbon (Vitreous), Type KEG Evaporating Dish, 20ml
| Availability | Contact for Availability |
|---|---|
| Item | 4268GCD-AB |
Glassy carbon is a unique material and exhibits properties entirely different from other forms of carbon with which one already has some high amount of familiarity. The glassy carbon dishes offered by SPI Supplies in Sigradur G Grade are plug-in compatible in many applications where presently only Pt evaporating dishes are being used. Their low economical cost, relative to platinum makes them especially in demand in days of shrinking research budgets. The very high density of the product literally prevents many molten materials from spreading on the glassy carbon surface. And the high density prevents any of the molten species from leaching into the glassy carbon surface.
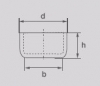
- Type: KEG 20
- Volume: 20 ml
- D: 46 mm
- B: 26 mm
- H: 20 mm
- Wall Thickness: 3 mm
Why the SPI-Glas Glassy Carbon Evaporating Dishes are so Popular:
The majority of our customers are using these glassy carbon evaporating dishes for wet decomposition procedures in analytical chemistry. Not only are they far lower is cost than platinum dishes, they are far less likely to "disappear", and they are more corrosion resistant and temperature resistant than platinum. For example, the SPI-Glas dishes are far more highly resistant to sodium peroxide. And of course, elements such as Fe, Cr, and Ni which would quickly alloy and ruin a platinum crucible won't have any noticeable effect on glassy carbon.
Chemical Resistance:
Theoretically, glassy carbon should behave like any other form of carbon, such as graphite, but in fact it is far less reactive because of the higher density relative to the normally more porous graphite. Its resistance is more akin to HOPG and high density pyrolytic graphite.
Thermal Properties:
The material can be taken to 3000° C without any significant devitrification. However above that temperature, some devitrification will occur, and there will be a nucleation and growth of a graphite phase.
Note: that the SPI Glas glassy carbon products can be heated in air up to 500° C without undergoing any reaction but above this temperature, any heating should be done strictly either under vacuum or in an environment of argon.